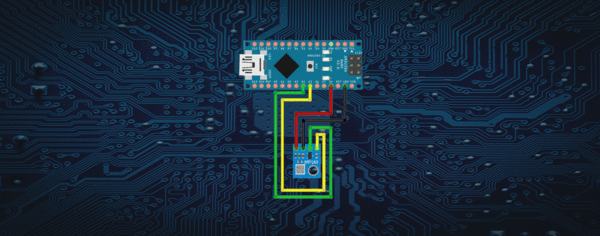
Heute wollen wir eine interessante Möglichkeit aufzeigen unseren BMP180 ohne extra Libary anzusteuern. Durch den verbauten Festspannungsregler ist unser BMP sowohl mit 3.3V als auch mit 5V kompatibel, allerdings werden die Werte unterschiedlich kalkuliert, so dass folgender Sketch nur mit 5V die richtigen Werte ausgibt. Die Verkabelung ist einfach:

und der dazugehörgie Code:
/*Based largely on code by Jim Lindblom Get pressure, altitude, and temperature from the BMP180. Serial.print it out at 9600 baud to serial monitor. */ #include <Wire.h> #define BMP180_ADDRESS 0x77 // I2C address of BMP180 const unsigned char OSS = 0; // Oversampling Setting // Calibration values int ac1; int ac2; int ac3; unsigned int ac4; unsigned int ac5; unsigned int ac6; int b1; int b2; int mb; int mc; int md; // b5 is calculated in bmp180GetTemperature(...), this variable is also used in bmp180GetPressure(...) // so ...Temperature(...) must be called before ...Pressure(...). long b5; void setup(){ Serial.begin(9600); Wire.begin(); bmp180Calibration(); } void loop() { float temperature = bmp180GetTemperature(bmp180ReadUT()); //MUST be called first float pressure = bmp180GetPressure(bmp180ReadUP()); float atm = pressure / 101325; // "standard atmosphere" float altitude = calcAltitude(pressure); //Uncompensated caculation - in Meters Serial.print("Temperature: "); Serial.print(temperature, 2); //display 2 decimal places Serial.println("deg C"); Serial.print("Pressure: "); Serial.print(pressure, 0); //whole number only. Serial.println(" Pa"); Serial.print("Standard Atmosphere: "); Serial.println(atm, 4); //display 4 decimal places Serial.print("Altitude: "); Serial.print(altitude, 2); //display 2 decimal places Serial.println(" M"); Serial.println();//line break delay(1000); //wait a second and get values again. } // Stores all of the bmp180's calibration values into global variables // Calibration values are required to calculate temp and pressure // This function should be called at the beginning of the program void bmp180Calibration() { ac1 = bmp180ReadInt(0xAA); ac2 = bmp180ReadInt(0xAC); ac3 = bmp180ReadInt(0xAE); ac4 = bmp180ReadInt(0xB0); ac5 = bmp180ReadInt(0xB2); ac6 = bmp180ReadInt(0xB4); b1 = bmp180ReadInt(0xB6); b2 = bmp180ReadInt(0xB8); mb = bmp180ReadInt(0xBA); mc = bmp180ReadInt(0xBC); md = bmp180ReadInt(0xBE); } // Calculate temperature in deg C float bmp180GetTemperature(unsigned int ut){ long x1, x2; x1 = (((long)ut - (long)ac6)*(long)ac5) >> 15; x2 = ((long)mc << 11)/(x1 + md); b5 = x1 + x2; float temp = ((b5 + 8)>>4); temp = temp /10; return temp; } // Calculate pressure given up // calibration values must be known // b5 is also required so bmp180GetTemperature(...) must be called first. // Value returned will be pressure in units of Pa. long bmp180GetPressure(unsigned long up){ long x1, x2, x3, b3, b6, p; unsigned long b4, b7; b6 = b5 - 4000; // Calculate B3 x1 = (b2 * (b6 * b6)>>12)>>11; x2 = (ac2 * b6)>>11; x3 = x1 + x2; b3 = (((((long)ac1)*4 + x3)<<OSS) + 2)>>2; // Calculate B4 x1 = (ac3 * b6)>>13; x2 = (b1 * ((b6 * b6)>>12))>>16; x3 = ((x1 + x2) + 2)>>2; b4 = (ac4 * (unsigned long)(x3 + 32768))>>15; b7 = ((unsigned long)(up - b3) * (50000>>OSS)); if (b7 < 0x80000000) p = (b7<<1)/b4; else p = (b7/b4)<<1; x1 = (p>>8) * (p>>8); x1 = (x1 * 3038)>>16; x2 = (-7357 * p)>>16; p += (x1 + x2 + 3791)>>4; long temp = p; return temp; } // Read 1 byte from the BMP180 at 'address' char bmp180Read(unsigned char address) { unsigned char data; Wire.beginTransmission(BMP180_ADDRESS); Wire.write(address); Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.requestFrom(BMP180_ADDRESS, 1); while(!Wire.available()) ; return Wire.read(); } // Read 2 bytes from the BMP180 // First byte will be from 'address' // Second byte will be from 'address'+1 int bmp180ReadInt(unsigned char address) { unsigned char msb, lsb; Wire.beginTransmission(BMP180_ADDRESS); Wire.write(address); Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.requestFrom(BMP180_ADDRESS, 2); while(Wire.available()<2) ; msb = Wire.read(); lsb = Wire.read(); return (int) msb<<8 | lsb; } // Read the uncompensated temperature value unsigned int bmp180ReadUT(){ unsigned int ut; // Write 0x2E into Register 0xF4 // This requests a temperature reading Wire.beginTransmission(BMP180_ADDRESS); Wire.write(0xF4); Wire.write(0x2E); Wire.endTransmission(); // Wait at least 4.5ms delay(5); // Read two bytes from registers 0xF6 and 0xF7 ut = bmp180ReadInt(0xF6); return ut; } // Read the uncompensated pressure value unsigned long bmp180ReadUP(){ unsigned char msb, lsb, xlsb; unsigned long up = 0; // Write 0x34+(OSS<<6) into register 0xF4 // Request a pressure reading w/ oversampling setting Wire.beginTransmission(BMP180_ADDRESS); Wire.write(0xF4); Wire.write(0x34 + (OSS<<6)); Wire.endTransmission(); // Wait for conversion, delay time dependent on OSS delay(2 + (3<<OSS)); // Read register 0xF6 (MSB), 0xF7 (LSB), and 0xF8 (XLSB) msb = bmp180Read(0xF6); lsb = bmp180Read(0xF7); xlsb = bmp180Read(0xF8); up = (((unsigned long) msb << 16) | ((unsigned long) lsb << 8) | (unsigned long) xlsb) >> (8-OSS); return up; } void writeRegister(int deviceAddress, byte address, byte val) { Wire.beginTransmission(deviceAddress); // start transmission to device Wire.write(address); // send register address Wire.write(val); // send value to write Wire.endTransmission(); // end transmission } int readRegister(int deviceAddress, byte address){ int v; Wire.beginTransmission(deviceAddress); Wire.write(address); // register to read Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.requestFrom(deviceAddress, 1); // read a byte while(!Wire.available()) { // waiting } v = Wire.read(); return v; } float calcAltitude(float pressure){ float A = pressure/101325; float B = 1/5.25588; float C = pow(A,B); C = 1 - C; C = C /0.0000225577; return C; }
So kann der BMP180 ressourcensparend eingesetzt werden und der Code ist für fortgeschrittene Benutzer leicht für andere Atmel Controller adaptierbar.









1 Kommentar
Achim
Erst einmal danke für den Beispiel-Code.
Zitat “ist unser BMP sowohl mit 3.3V als auch mit 5V kompatibel, allerdings werden die Werte unterschiedlich kalkuliert”.
Wenn auf der Platine ein Festspannungsregler ist, frage ich mich, warum die Werte unterschiedlich kalkuliert werden?